Introduction
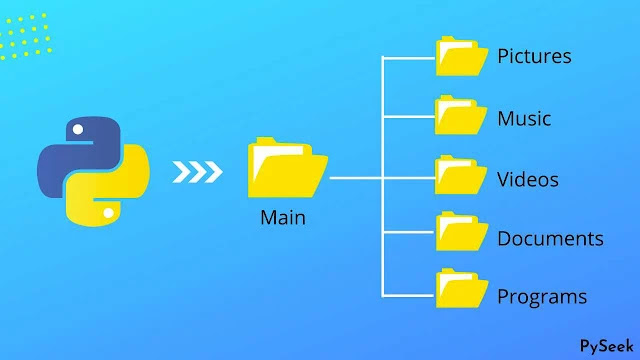
Today we are gonna solve a real-life problem using our favorite programming language Python. Let's talk about the problem first. Have you ever noticed one thing after downloading different types of files from the Internet, how your default 'Downloads' folder looks? In most cases, it may look like a mess.
Not only you, but every computer user may also have faced this problem more or less. The situation gets so bad that when we try to find a specific file there it becomes quite spiny to find.
But, in today's lesson, I came up here with a solution for this problem. I create a Junk File Organizer in Python that will automatically organize any messy folder in such a way: all the photos will be placed in the 'Pictures' folder, videos in the 'Videos' folder, all documents in the 'Documents' folder, in 'Audios' all the audio file, and so on.
I gave a User Interface to this application using Python Tkinter Library. All you have to do is select the folder (which you want to sort) through a Tkinter Widget (File dialog) and the program will sort your selected folder in a well manner in a blink of an eye.
Let's get into the main topic.
👉Visit Also: Rename Multiple Files using Python (Tkinter Project)
Requirements
Before start writing the code, make sure you have installed these libraries.
☛Install Tkinter: pip install tk
☛Install Pillow: pip install Pillow
Pillow is an open-source Python imaging library that provides many functions or methods for performing various operations with images using Python.
I have set a logo on this File Organizer Application to give it a beautiful look. There this pillow library has played a major role in this work.
How does this application work?
This application is very easy to use. You just need to select the folder(or you can enter the folder path to the Entry widget too) through a button. Next, press the 'Start' button; the program will organize all the files present in that folder in a neat and tidy form.
Do watch this output video to understand it better.
Import the modules
Let's create a Python file with the name "File_Organizer.py" and start writing your code by importing these modules. You can choose another name as your choice. I kept this name by following the objectives of the program.
import os
import shutil
from tkinter import *
from threading import *
from PIL import ImageTk, Image
from tkinter import messagebox, filedialog
Declare a dictionary of Extensions
Now declare a python dictionary that contains an extensions list(as the Value of each Key) matching with the corresponding Key name.
# Modification can be performed here.
# You can add more extensions to this dictionary
Extensions={
'Documents' : ('.pdf','.doc','.xls','txt','.csv','.zip',\
'.xml','.zip', '.docx', '.DOCX', '.odt'),
'Pictures' : ('.jpg','.jpeg','.png','.JPG'),
'Videos' : ('.mp4','.mkv','.3gp','.flv','.mpeg'),
'Music' : ('.mp3','.wav','.m4a','.webm'),
'Programs' : ('.py','.cpp','.c','.sh','.js'),
'Apps' : ('.exe','.apk'),
}
Declare the 'File_Organizer' class
Declare a 'File_Organizer' class.
class File_Organizer:
Declare the __init__() function
It will create a GUI window for us. We set the window size, title, background color, resizable option, etc. here.
In this function, I've declared two Tkinter frames, two buttons, and some variables that are gonna used in the upcoming program. Later this function calls the 'Main_Page()' and 'Display_Logo()' functions.
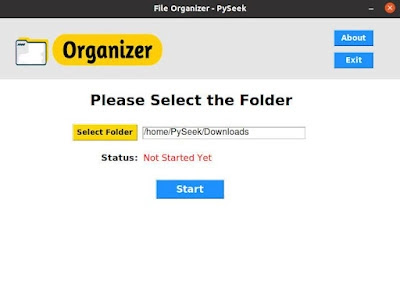 |
| Image - File Organizer Application |
def __init__(self, root):
# Setting the Tkinter main window
self.window = root
self.window.geometry("720x500")
self.window.title('File Organizer - PySeek')
self.window.resizable(width = False, height = False)
self.window.configure(bg='gray90')
self.Selected_Dir = ''
self.Browsed = False
# Frame 1: For the Logo
self.frame_1 = Frame(self.window,bg='gray90',\
width=280, height=70)
self.frame_1.pack()
self.frame_1.place(x=20, y=20)
# Calling the function to display the logo
self.Display_Logo()
# About Button
About_Btn = Button(self.window, text="About", \
font=("Kokila", 10, 'bold'), bg="dodger blue", \
fg="white", width=5, command=self.About_Window)
About_Btn.place(x=600, y=20)
# Exit Button
Exit_Btn = Button(self.window, text="Exit", \
font=("Kokila", 10, 'bold'), bg="dodger blue", \
fg="white", width=5, command=self.Exit_Window)
Exit_Btn.place(x=600, y=60)
# Frame 2: For the Main Page Widgets
self.frame_2 = Frame(self.window, bg="white",\
width=720,height=480)
self.frame_2.place(x=0, y=110)
# Calling the function to display main page
# widgets
self.Main_Page()
Display the logo
This function displays a logo in the header section of the window. It gives the application a pro look. Here, the image location(or path) is mentioned in the Image.open() function. The image file must need to present there; otherwise, the program will give an error message.
 |
| Image - The Logo |
# This function displays the File Organizer Logo
def Display_Logo(self):
# Opening the logo image
image = Image.open('Images/File_Organizer.png')
# Resizing the image
resized_image = image.resize((280, 70))
# Create an object of tkinter ImageTk
self.img_1 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(resized_image)
# Create a Label Widget to display the text or Image
label = Label(self.frame_1, bg='gray90',image=self.img_1)
label.pack()
The main page
The 'Main_Page()' function displays all the widgets related to performing junk folder organizing. For example, the 'Select Folder' button(for selecting the messy directory through the Tkinter File Dialog), an Entry widget(users can enter the directory/folder path directly here), a Status Label(for showing the current status of the operation), and a 'Start Button' to operate.
I've declared one single comment line before each segment of the code. It will help you to understand the objectives of this piece of code better.
# This function displays all the widgets in the 'self.frame_2'
# related to File Organizing Operation
def Main_Page(self):
# Heading Label
Heading_Label = Label(self.frame_2, text="Please Select the Folder", \
font=("Kokila", 20, 'bold'), bg='white')
Heading_Label.place(x=160, y=20)
# Button for selecting the directory(where
# the desired files are presented)
Folder_Button = Button(self.frame_2, text="Select Folder", \
font=("Kokila", 10, 'bold'), bg="gold", width=10, \
command=self.Select_Directory)
Folder_Button.place(x=130, y=80)
# The directory path selected from the Tkinter file dialog
# that opens by the 'Folder_Button' is displayed here.
self.Folder_Entry = Entry(self.frame_2, \
font=("Helvetica", 12), width=32)
self.Folder_Entry.place(x=256, y=85)
Status = Label(self.frame_2, text="Status: ", \
font=("Kokila", 12, 'bold'), bg='white')
Status.place(x=180, y=130)
# Status Label:
# Options: 'Not Started Yet(By Default), or 'Processing...',
# or 'Complete!''
self.Status_Label = Label(self.frame_2, text="Not Started Yet", \
font=("Kokila", 12), bg="white", fg="red")
self.Status_Label.place(x=256, y=130)
# Start Button: Users have to press this button
# to start the operation
Start_Button = Button(self.frame_2, text="Start", \
font=("Kokila", 13, 'bold'), bg="dodger blue", fg="white", \
width=8, command=self.Organizer)
Start_Button.place(x=280, y=180)
Select the directory
'Select_Directory()' function will let you select that folder(through the file dialog) that you want to organize. When the 'Folder_Button' is pressed this function gets a call.
# This function opens the Tkinter file dialog to
# let users select the directory where the files are presented
def Select_Directory(self):
self.Selected_Dir = filedialog.askdirectory(title = \
"Select a location")
# Insert the folder path to the Entry Box
self.Folder_Entry.insert(0, self.Selected_Dir)
# Converting the type of 'self.Selected_Dir' variable
# to String for avoiding any error while checking
# the path exists or not
self.Selected_Dir = str(self.Selected_Dir)
# Checks if the folder path is exists or not
if os.path.exists(self.Selected_Dir):
self.Browsed = True
Create a different Thread and call the 'Organizer()' function
The 'Threading()' function creates a different thread for calling the 'Organizer()' function to complete the main task. I've added the necessary comment lines before each line of the code. I hope it will help you to grab the logic of this part.
# Creating a different thread to run the 'self.Organizer' function
def Threading(self):
# Killing a thread through "daemon=True" isn't a good idea
self.x = Thread(target=self.Organizer, daemon=True)
self.x.start()
# The Organizer function
def Organizer(self):
# If no directory is chosen
if not self.Browsed:
messagebox.showwarning('No folders are choosen', \
'Please Select a Folder First')
return
try:
# Showing the current status of the operation
self.Status_Label.config(text='Processing...')
self.Current_Path = self.Selected_Dir
if os.path.exists(self.Current_Path):
# self.Folder_List1: stores all the folders that
# are already presented in the selected directory
self.Folder_List1 = []
# self.Folder_List2 stores newly created folders
self.Folder_List2 = []
self.Flag = False
for folder, extensions in Extensions.items():
self.folder_name = folder
self.folder_path = os.path.join(self.Current_Path, self.folder_name)
# Change the directory to the current
# folder path that we've selected
os.chdir(self.Current_Path)
# If the folder is already present in that directory
if os.path.exists(self.folder_name):
self.Folder_List1.append(self.folder_name)
# If the folder is not present in that directory,
# then create a new folder
else:
self.Folder_List2.append(self.folder_name)
os.mkdir(self.folder_path)
# Calling the 'File_Finder()' function to
# find a specific type of file(extension)
# and change their old path to new path(for separation)
for item in self.File_Finder(self.Current_Path, extensions):
self.Old_File_Path = os.path.join(self.Current_Path,item)
self.New_File_Path = os.path.join(self.folder_path,item)
# Moving each file to their new location(folder)
shutil.move(self.Old_File_Path, self.New_File_Path)
# Making the 'self.Frag' variable True
self.Flag = True
else:
messagebox.showerror('Error!','Please Enter a Valid Path!')
# Checking files are separated or not
# If Flag is True: It means the program had found
# some matching files and those have been organized
if self.Flag:
self.Status_Label.config(text='Complete!')
messagebox.showinfo('Done!', 'Complete!')
self.Clear()
# If Flag is False: It means the program didn't find
# any matching files there; only folders are created
if not self.Flag:
self.Status_Label.config(text='Complete!')
messagebox.showinfo('Done!', \
'Folders have been created\nNo Files were there to move')
self.Clear()
# If any error occurs
except Exception as es:
messagebox.showerror("Error!",f"Error due to {str(es)}")
Declare a function called 'File_Finder()'
This function gets a call from the previous function. It finds a specific file type in the selected directory and appends the matched file path to this 'self.files' list, and returns it.
# This function finds a specific file-type in
# the selected directory, appends the matched file path
# to a list, and returns that list
def File_Finder(self,folder_path, file_extensions):
self.files = []
for file in os.listdir(folder_path):
for extension in file_extensions:
if file.endswith(extension):
self.files.append(file)
return self.files
The Clear function
This 'Clear()' function will reset these 'self.Status_Label' and 'self.Folder_Entry' widgets, and the 'self.Selected_Dir' variable after completing the task.
def Clear(self):
self.Status_Label.config(text='Not Started Yet')
self.Folder_Entry.delete(0, END)
self.Selected_Dir = ''
The miscellaneous functions
Here, we'll declare two functions. When the 'About' and 'Exit' button is pressed(present in the header section of the application) these two('About_Window()', and 'Exit_Window()') functions will get a call respectively.
# When the 'About' button is pressed, this function gets a call
def About_Window(self):
messagebox.showinfo("File Organizer 22.05",\
"Developed by Subhankar Rakshit\n~PySeek")
# This function closes the main window
def Exit_Window(self):
self.window.destroy()
The main function
Now it's time for the main function. Here, we will create a Tk() class object, and a 'File_Organizer' class object. The Tkinter event loop(mainloop) will start running from here.
# The main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Tk()
# Creating a 'File_Renamer' class object
obj = File_Organizer(root)
root.mainloop()
Download the Project
Download the source code of this project from my GitHub page(https://github.com/subhankar-rakshit) through the download button.
Summary
In this tutorial, we build a Junk File Organizer in Python that can sort out an unorganized folder in a neat and tidy form. This application can be used by anyone because of its easy graphical interface even if the user is a non-programmer; only the requirements required by the project must be met.
There are more lovely Python Projects that I have created with the Tkinter library. Here are some examples of them.
👉An Advanced Alarm Clock using Python Tkinter
👉Image to Cartoon Converter using Python
👉An Image Viewer Application using Python Tkinter
I hope you loved this tutorial. You're also welcome to give me any further suggestions to improve this Application. You can share your opinion in the comment section.
Thanks for reading!💙
PySeek